You may be unsure of what image file format is correct for your document, print or electronic, for a particular task. The following information on image file formats and their uses should help answer your questions as to which is best in a particular situation. When in doubt, it is best to ask a professional for help. The time saved and the quality gained will be well worth it in the final impression that you make.
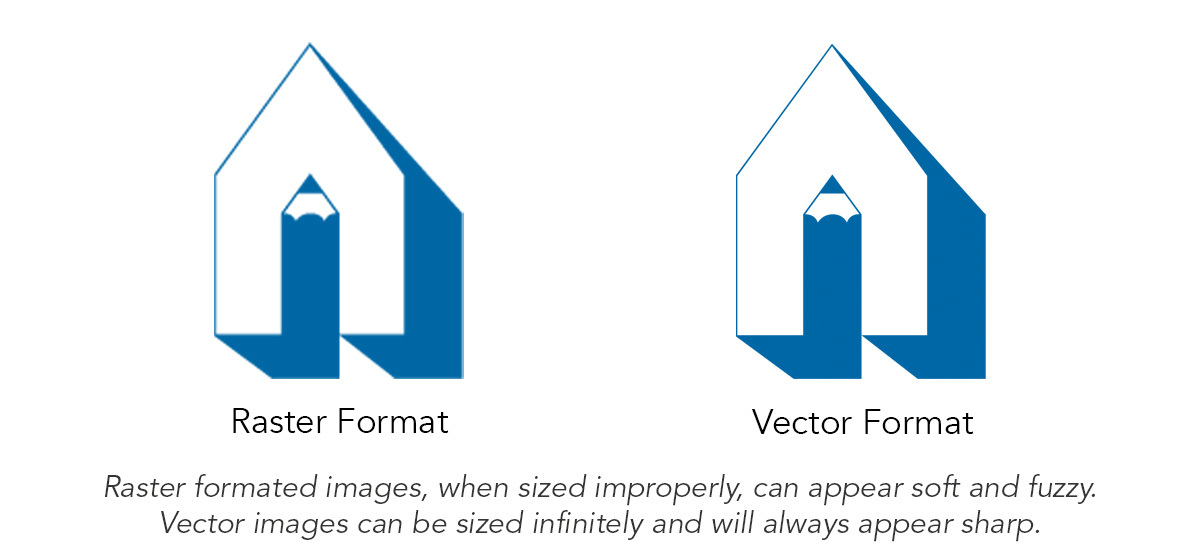
Raster Formats
Raster formatted images are made up of pixels and are not infinitely scalable. Their quality will degrade proportionately with any increase in size larger than the original. Raster graphics can be successfully reduced in size. The advantage of a raster format is its ability to portray continuous tone images like photographs and gradient tints of color where the edges of the image are contained in a square or rectangular shape or bleed off the edge of the page. Raster images are also commonly used on the web.
Examples of raster formats are:
- JPEG (.jpg) Solid background unless used with a mask or clipping path
- TIFF (.tif) May be transparent if prepared and saved that way
- PNG (.png) May be transparent if prepared and saved that way
- GIF (.gif) Solid background, may be animated
- BMP (.bmp) Raster graphic format for saving images in the Windows format
Vector Formats
Vector formatted images have outlines and are typically drawn in an illustration program like Adobe Illustrator. The advantage of a vector file format is that it can be scaled infinitely without loss of sharpness or detail. Vector images can easily be saved with transparent or solid backgrounds.
Examples of vector formats are:
- AI (.ai) Native Adobe Illustrator Format, transparent background, infinitely scalable
- EPS (.eps) Encapsulated Postscript Format, transparent background, infinitely scalable
- PDF (.pdf) Portable Document Format, a vector PDF can be transparent, infinitely scalable
- SVG (.svg) Scalable Vector Graphic, can have a transparent background, infinitely scalable
There are many nuances to choosing one file format over another. If you are interested in learning more details about file formats, there are numerous websites dedicated to defining file formats and their uses on the internet. The basic differences are outlined above.
